NVIDIA RTX 5070 Ti Suffers from Missing ROPs, Affecting Performance
The unveiling of NVIDIA's GeForce RTX 5070 Ti has been marred by the revelation of hardware defects in some units, primarily involving an unexpectedly lower number of Raster Operating Units (ROPs) than the official specifications indicate. This defect is not confined to the RTX 5070 Ti but also affects high-end models like the RTX 5090 and RTX 5090D, sparking widespread discussion in the tech community.

User-shared GPU-Z screenshots on social media display that some RTX 5070 Ti units only feature 88 ROPs instead of the 96 claimed by the official specs, marking a reduction of about 8.4 percent. ROPs are crucial for the GPU rendering pipeline and significantly impact pixel fill rate and overall graphics performance. According to official data, an RTX 5070 Ti featuring the full 96 ROPs can achieve a pixel fill rate of up to 287.7 GPixel/s. In contrast, the flawed versions manage only 223.7 GPixel/s at lower frequencies. Even if the boost clock is pushed to 2.99 GHz, the fill rate increases only to 263.12 GPixel/s, which remains about 9% lower than the standard model. Therefore, the performance shortfall becomes more apparent during graphically demanding tasks.
In response, NVIDIA acknowledged that around 0.5% of RTX 5090, 5090D, and 5070 Ti cards suffer from deficient ROP counts, estimating an average performance drop of roughly 4%. However, the tangible impact varies based on the application: in games or benchmarks heavily reliant on ROPs, the drop could reach 11%, while in other contexts, the difference might be negligible. The company attributed the problem to a production anomaly, which has since been rectified and advised affected users to contact their board makers for replacements. Despite the seemingly minor 0.5% defect rate, given the RTX 50 series' shipment volumes, this could encompass thousands of graphics cards.
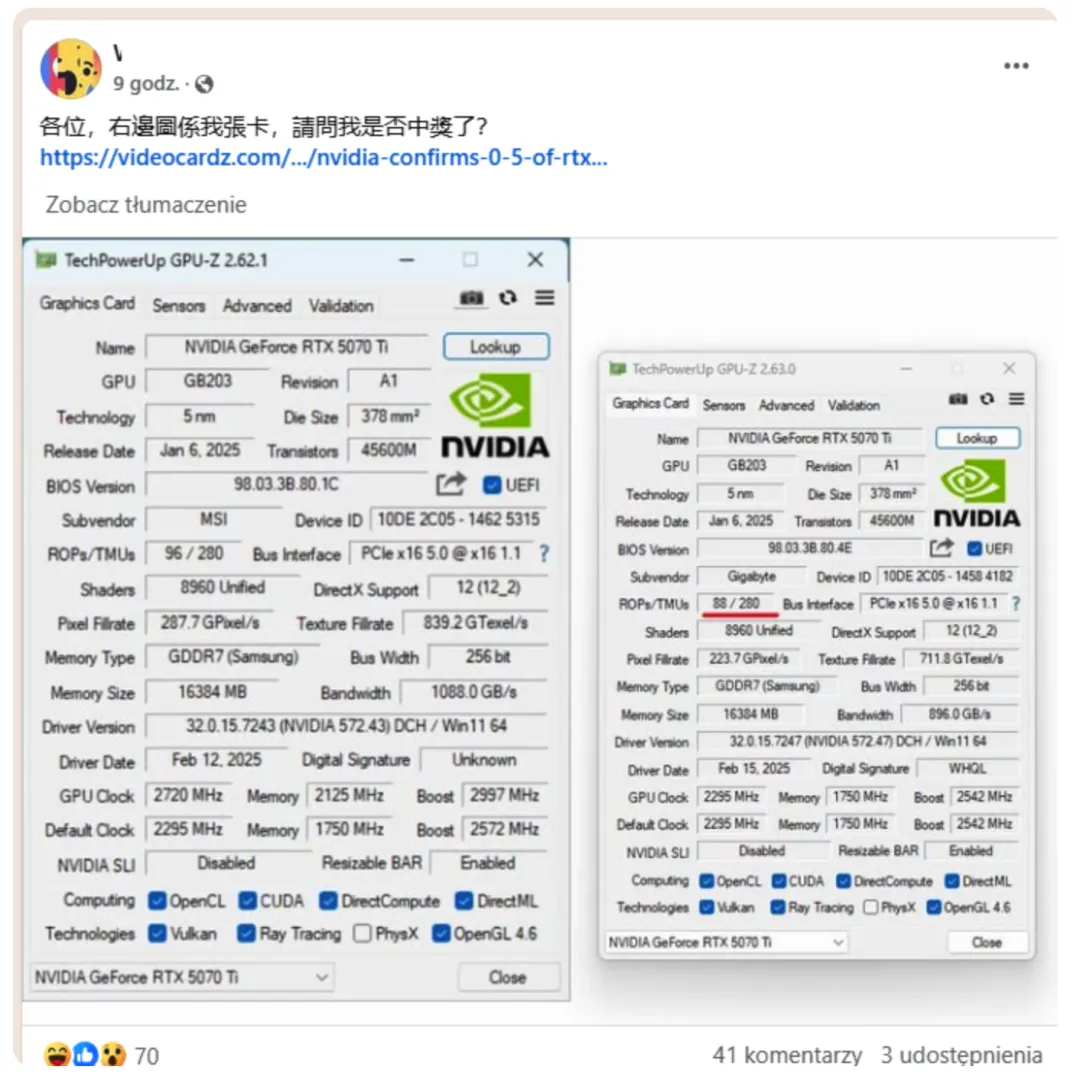
The RTX 5070 Ti, leveraging NVIDIA's latest Blackwell architecture, comes equipped with 8,960 CUDA cores, 70 RT cores, and 16GB of GDDR7 memory, offering a memory bandwidth of 896GB/s. It targets the high-end gaming market and enters it with an official price of $749 (CNY 6,299 in China), notably more appealing compared to its predecessor, the downgraded RTX 4070 Ti Super, priced at $799. However, the current ROP discrepancies cast a shadow on its reliability. Users can conveniently verify the number of ROPs on their cards via GPU-Z, confirming any flawed versions if the count falls short of 96.
Adding to user concerns, the availability of RTX 50 series cards remains uncertain. Thai retailers, for instance, have forecasted potential delays for models like the RTX 5070 Ti extending to July 2025. This supply constraint deepens consumer fears that even if faulty cards are detected, obtaining replacements might prove challenging due to limited stock. Additionally, reports from some RTX 5090 users experiencing issues like melted power connectors suggest risks associated with newer graphics card purchases.
Technically, reducing the ROP count directly impairs a graphics card's rendering capacity, especially in high-resolution gaming scenarios, such as 4K environments and ray tracing. In popular games like Cyberpunk 2077, with ray tracing and DLSS 4 enabled, the standard RTX 5070 Ti is capable of delivering fluid frame rates at 1440p resolution, but defective versions could experience latency or frame dips. NVIDIA asserts that, thanks to DLSS 4’s multi-frame generation technology, the RTX 5070 Ti’s performance can be up to twice that of earlier models.
The issue is not isolated to the RTX 5070 Ti; the RTX 5090 also suffers a reduction in ROPs, from 176 to 168, paralleling the 5070 Ti’s performance decline. This situation highlights potential production and quality control oversights on NVIDIA’s part. While NVIDIA assures that the fraction of affected products is minimal and bears negligible effects on AI and computational tasks, gaming enthusiasts focused on peak performance might find any compromise untenable.

NVIDIA’s RTX 5070 Ti, now officially available since February 20, 2025, inaugurates the Blackwell series alongside the RTX 5090 and 5080 models. The standard version boasts 28Gb/s GDDR7 memory, a 256-bit memory bus, and supports cutting-edge DisplayPort 2.1a and HDMI 2.1b interfaces, consuming approximately 300W of power. This performance boost over the RTX 4070 Ti Super (285W) attributes primarily to architectural enhancements and AI-driven tech. Continued scrutiny over the ROP issue may sway consumers towards the upcoming RTX 5070 or AMD’s Radeon RX 9070 XT.
How NVIDIA manages its stock and facilitation of replacement processes amid these challenges with consumer trust and supply shortages will critically test its after-sales service competence. Evidently, the launch of the Blackwell series has faced an unexpectedly rocky start.
Related News
- NVIDIA is Preparing to Launch a Gaming Laptop APU Equivalent to the 4070
- Leaked Benchmark Data for AMD RX 9060XT Shows It Underperforming Compared to 5060Ti
- Intel Official Website Unveils Arc B750 Graphics Card
- Rumor Has It: Intel to Launch Arc B770 Graphics Card Later This Month
- Xe3 Is Not Yet Launched, But Xe4 Is Already on the Horizon: Intel Moves Quickly
- Intel to Launch Next-Generation Arc Battlemage Graphics Card with 24GB VRAM
- The Anticipation Ends: Intel Set to Launch B770 Independent Graphics Card
- Are Nvidia and AMD Set to Unveil Mysterious New Cards Next Month?
- AMD Soon to Release a New Wave of RX 9000M Laptop Graphics Cards
- NVIDIA RTX 5060Ti Specifications Revealed: Double-Digit Performance Boost Over Previous Generation